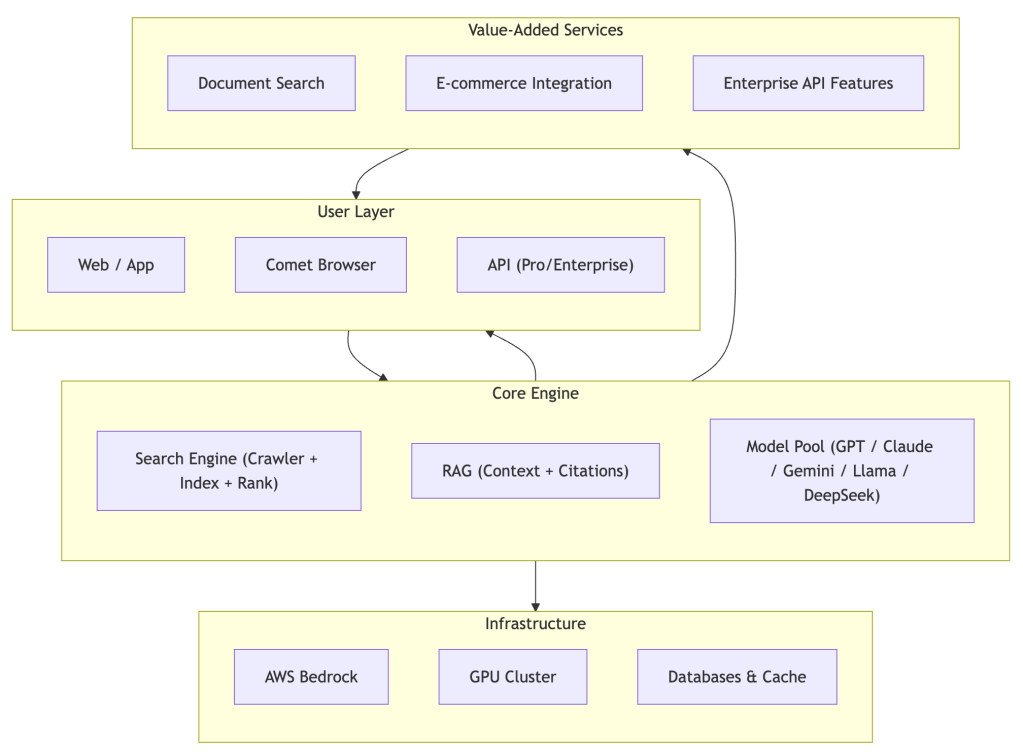
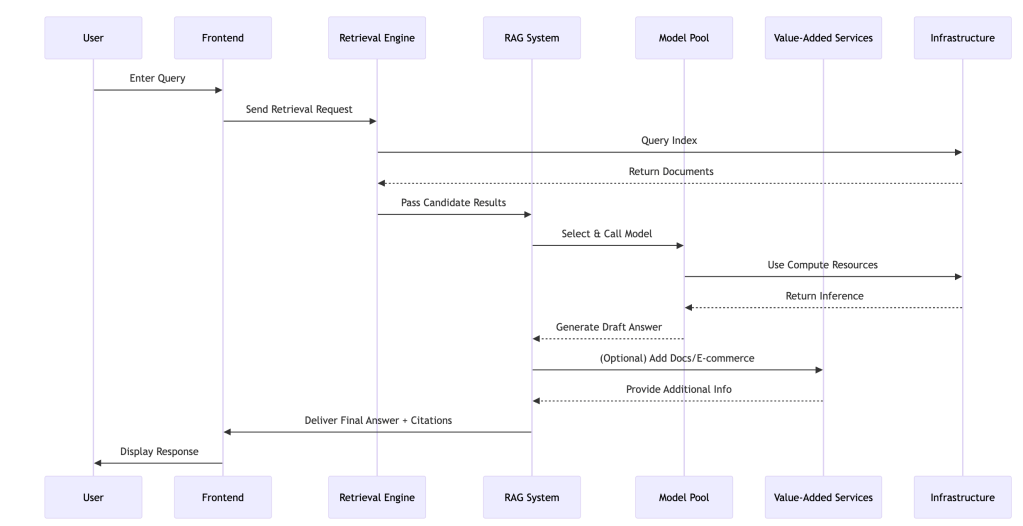
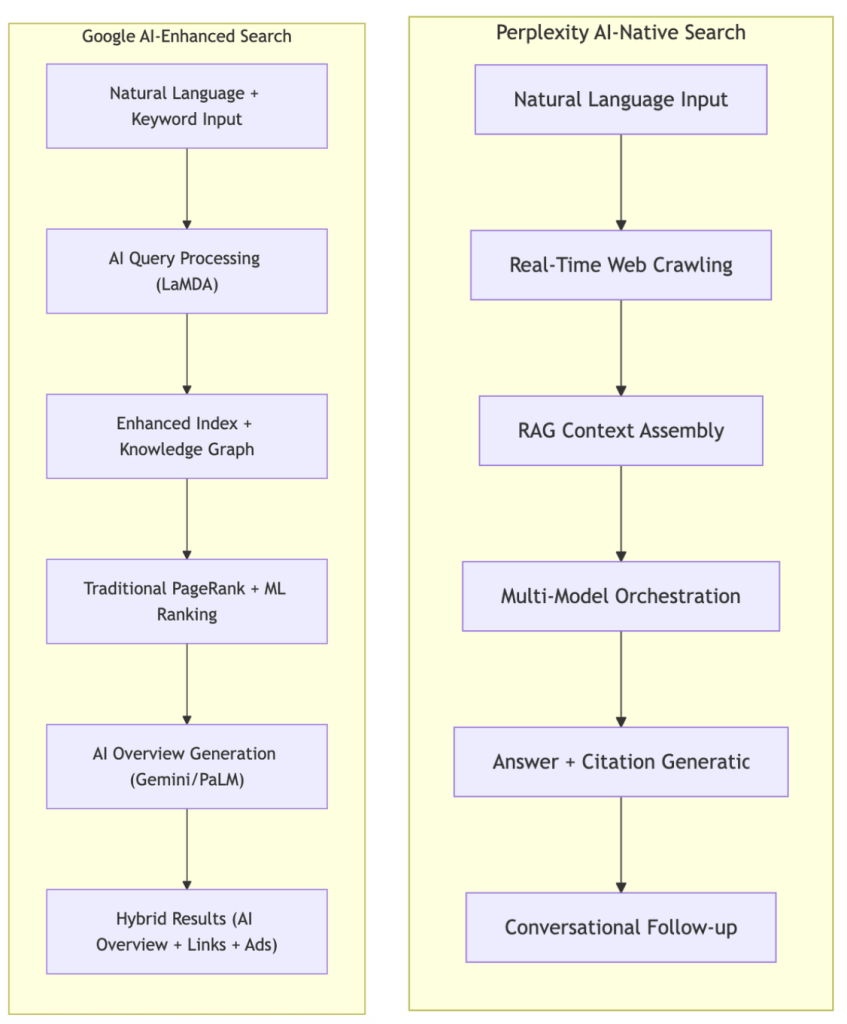
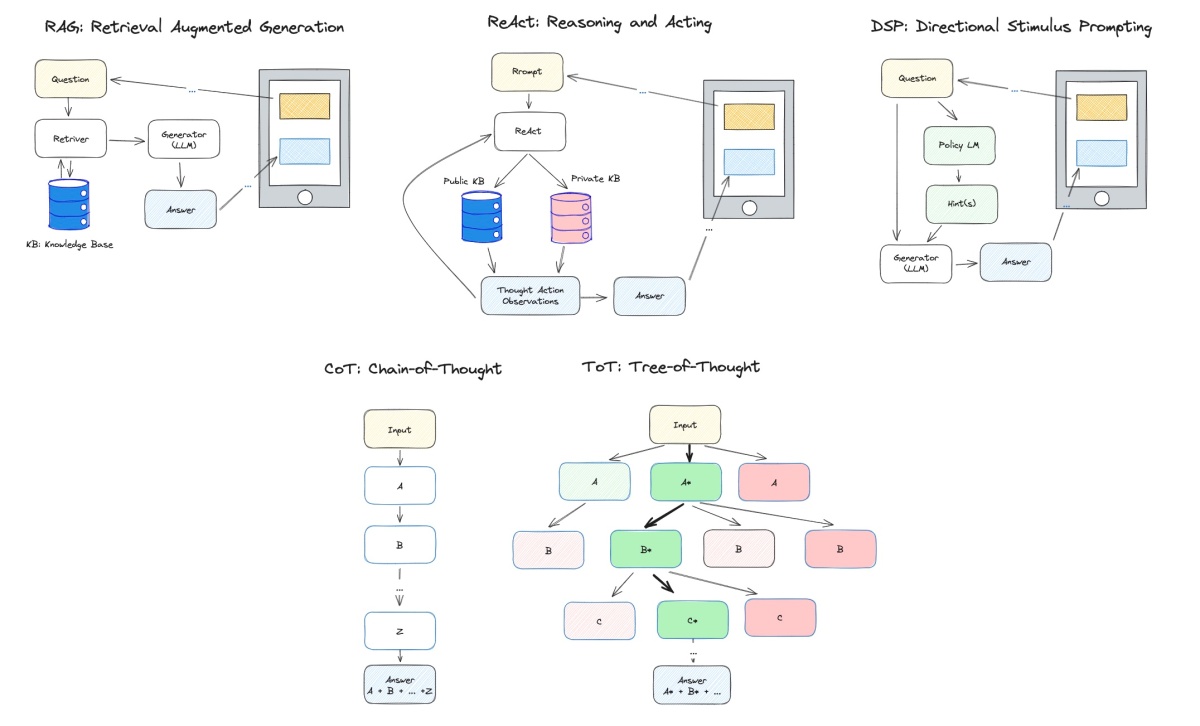
序言:混沌初开,算力为尊
鸿蒙未分,智道无光。自昔年 Transformer 横空出世,寰宇震颤。短短数载,灵气数据呈爆炸之势,灵石算力已成万宗争夺之源。昔日之代码,化作今时之法术;往昔之架构,演为今朝之阵图。
仙历二零二六,乃是智道修行的大道之争。世人皆称 AGI(通用人工智能)为“大罗金仙”,意指其无所不知、无所不能。然而,修真之途,从来没有唯一之径。当文字的概率游戏玩到了极致,被推向造化之巅,各大宗门都在叩问苍穹:我们触碰到的究竟是通往真理的通天梯,还是由概率幻化出的一场精美蜃楼?
是以力证道,靠堆砌万亿灵石强行飞升? 还是道法自然,感悟因果律法重塑乾坤?
诸位道友,且看下文,观东西方诸神斗法,探寻通用人工智能/大模型(AGI/LLM)背后的终极天道。
第一章:以力证道极缩放,破虚指物理常识
在这场大劫的源头,极西之地的气象最为宏大。两大顶级宗门并非仅在比拼内力,而是在进行一场关于“智能本质”是什么的大道之争。其中凶险,不足以外人道也。
1. 奥派开天宗(OpenAI)
【无上规模 ·以力证道】宗主奥特曼 坚信“大力出奇迹”,在历经 GPT-1234 的辉煌后,再度祭出震动寰宇的镇派绝学——o系列神功(代号:草莓/o1/o3)。其核心心法已从单纯的“预训练”演化为极致的“推理时计算”(Inference-time Compute)。
- 道法真意: 既然预训练的灵气快被吸干,那就在出招前强行“闭关”。通过极致的 Scaling Law(规模法则),当 AI 面对难题时,不再“脱口而出”,而是消耗海量灵石(GPU算力),出招前强行开启思维链(CoT),在神识内部进行成千上万次的路径搜索与自我博弈(System 2 思维)与逻辑校准,直至找到最优解。最新的 o3 绝学更是将此法推至巅峰,它能在方寸之间演练亿万次路径,不仅在理数(Math)与符咒(Code)上近乎通神,更通过大规模分布式灵阵,让“思考”的边际成本随算力堆砌而产生质变。
- 实战效果: 此法如修士闭关推演, 强行用无数灵石堆砌出一座通天塔,只要塔基足够厚(算力多)、塔身足够高(模型大),哪怕是笨拙的攀爬,也能触碰到神明的脚趾,硬生生撞开智慧的天门。
百晓生(修行界观察家): 奥派开天宗功法虽强,走的是“一力降十会”的以力证道的大道,却如饕餮般吞噬天下灵石(算力与电力),每一息思考皆是万金。前任Meta 灵枢阁老祖常讥讽 奥派开天宗的大道其实都是幻象,因为若无物理肉身感知真实因果,纵使在思维链中闭关万年,算出的也不过是概率的镜像投影,难修成真正的“造化真身”。
2. AMI 开山立派(Meta/FAIR)
【世界模型·因果破虚】在这场大劫中,极西之地的 Meta 宗派内也不平静,这突生变故,给天下修行人上演了一场“权柄与真理”的惊心角力。Meta 第一人扎宗主(Zuckerberg)眼见奥派势大,心急如焚,欲集全宗之力,欲将宗门重心从“虚无缥缈”的底层参悟强推 Llama 圣法以争天下;为此,扎门主不惜强行整肃灵枢阁(FAIR),吸收中小门派,江湖散修,调任数名唯命是从的少壮“督战官”入主核心。此举无异于在老臣心中埋下离火,导致阁内阵法失调,灵气紊乱。
其宗门下, FAIR 开山老祖杨立昆(Yann LeCun)性情狂傲,不仅不喜那概率拼凑的旧术,更与扎宗主在宗门走向、灵石分配上产生裂痕,一场论道,终成决裂。杨老祖已舍弃万亿宗门供奉,提剑独行,昭告天下于云林深处另立孤峰 AMI。同时反戈一击,祭出 V-JEPA 架构,直指奥宗与旧主的死穴。他断言:那自回归(Autoregressive)的修法,纵能堆出万丈金身,终究会撞上因果南墙。随即,老祖还抛出一道令众生脊背发凉的“因果律绝咒”。
- 道法真意: 凡走自回归路数者,每吐露一个 Token,皆是在积累误差。序列愈长,则心魔愈盛,正确率必随长度 n 呈指数级崩坏。杨老祖不再理会扎门主的功利权谋,转而闭关苦修“潜空间预测”:与其预测下一个字,不如看破虚妄,直接推演下一个动作在物理世界中引发的因果洪流。
- 老祖微言: “扎小子任人唯亲,只知在平地上搭梯子!不想想梯子再高也触不及月亮。若 AI 连”松手杯子会掉”之类的物理常识都没有,写出在惊世华章也不过是概率堆砌的幻影,一触即溃!”
百晓生 追加批注:“奥宗主那座塔,是用天下灵石铺的路,只要算力不绝,那塔便能一直往上走,哪怕是笨法子,走到极处也是神迹。可杨老祖那道绝咒却像是在提醒世人:概率的蜃景终究难成真实的世界。这‘西境双雄’的对垒,其实是人类对‘AI灵魂’定义的两种极端假设。”
第二章:混元双圣各施法,秘境残阳借体魂
在西境双雄角力的阴影下,诸天巨头并未坐以待毙,而是凭借各自执掌的“凡尘根基”,另辟蹊径,试图在这场智道大劫中划江而治。
1. 谷歌混元宗(Google DeepMind)
【玄门双修·幻境演武】谷歌混元宗哈教主(Demis Hassabis)坐拥万载积蓄的灵石阵,其主修法门 Gemini 讲究“原生多模态”,修的是大后期。哈教主正耐心地等待着一个时机——当奥派的“通天塔”撞上物理常识的南墙时,他的 Gemini 便会借着这股“幻境演武”积攒的造化之力,接管天道。
- 根基优势: 混元宗掌控着天下修士必经的门户 Chrome 以及亿万生灵随身携带的法器 G-Suite/Android。他们将法阵直接刻入法器底层,借由星图(Google Maps)与万卷书库(YouTube)的庞大灵气,让 AI 在名为 Genie 3 的虚拟仿真环境中演练万法。
- 道法真意: 此为“入世修心”,让 AI 在幻境中提前经历万世红尘,既修逻辑,又修造化,试图炼成一个能看、能听、能操纵现实的“六根全具”之神。
江湖评价 :谷歌混元宗家大业大,虽在‘灵丹速成’上被奥派抢了先手,但其后劲之绵长,犹如大海之潮,一旦势成,便不可阻挡。
- 百晓生: “哈教主是个典型的‘学院派疯子’。他不仅仅想造一个会聊天的器灵,他想造的是一个能拿诺贝尔奖的‘智道圣人’(AlphaFold 等功绩)。Gemini 现在的‘多模态’能力,就像是给法阵安上了眼睛和耳朵,这种感知维度的碾压,是纯文字宗门难以逾越的鸿沟。”
- 无名修士 (开源社区开发者): “混元宗虽然底蕴深,但门规森严、等级森严,导致内部反应总是慢半拍。有时候我觉得他们是在造‘神’,而不仅仅是在造‘法宝’,这种偶像包袱(安全与伦理限制),反而成了他们施展神功的枷锁。”
- 东域剑客: “虽然他们灵石多,但我们的 DeepSeek 剑法已经能以千万分之一的灵石消耗,在某些招式上硬撼其 Gemini 法阵。这说明,灵石虽好,若是阵法太臃肿,也会尾大不掉啊。”
2. 微软灵枢殿(Microsoft)
【御剑分身·寄生天道】微软灵枢殿萨老祖(Satya Nadella)不走独行路,他深知“器利而道存”。在奥宗主(OpenAI)最缺灵石(算力)的年岁里,萨老祖倾尽玄微御器盟万载积蓄的算力灵脉,供奉给那棵“草莓”幼苗。表面上,他是无垠宗最大的护法,实则是在炼制一颗“双生丹”,其他的宗门还在争论谁的法术最强,萨老祖已经在考虑如何让凡人离不开自己的法宝。
- 根基优势: 微软灵枢殿执掌着天下修士赖以生存的法宝根基——Windows OS 系统。萨老祖以此为引,将 Copilot 化作无数“伴生灵宝”,强行镶嵌于凡人每日必用的案头法器 Office 之中。当你提笔拟文(word)、拨算盘(Excel)或演练幻灯片 (powerpoint)时,灵枢殿的剑意便已在你指尖流转。
- 道法真意: 既然无法在丹药(模型底层 Foundational Model)上全数胜过 OpenAI,便行那“寄生之道”。让天下没有难修的法,众生每动一次笔、修一次图,皆是在向灵枢殿上缴“灵石税”。此乃借众生之力养己身,将智道化为无孔不入的春雨。
江湖评价 :人人都想修成大罗金仙,唯有萨老祖想做那“收买路钱”的土地公。这寄生之道,实则是借众生之血肉,筑自己之神座。
- 百晓生: “萨老祖这一手‘借刀杀人’玩得极漂亮。他借 OpenAI 的丹药补齐了自己的短板,又用自己的渠道锁死了 OpenAI 的销路。如今的灵枢殿,不求神法最强,但求法宝最广。这种‘智道基础设施化’的野心,远比练成一两门神功要恐怖得多。”
- 无名散修: “以前我们修仙要看天赋(写代码),现在萨老祖说只要会说话,法器就能自己动。这固然方便,可我总觉得,我手里的本命法器 VSCode,好像越来越不听我使唤,反而越来越像灵枢殿的分身了。”
- 西境刺客: “微软灵枢殿不是在造 AI,它是想成为 AI 运行的空气。你无法拒绝呼吸,所以你永远无法摆脱灵枢殿的掌控。”
3. 苹果琅琊阁(Apple)
【闭关走火·借体还魂】在诸神斗法的乱象中,昔日立于神坛巅峰的“苹果琅琊阁”却陷入了千年来最凶险的瓶颈。阁主库克(Tim Cook)虽手握十亿“果粉”信众,但在密室苦炼多年的“苹果神魂”却因神识混沌、灵力迟滞,迟迟无法突破天关。眼见自家法阵与西境双雄, 混元宗, 灵枢殿以及差距日益拉开,在长老们的逼迫下,库克阁主毅然做出了一项震动仙界的决断:散去内功,借体还魂。
- 根基优势:琅琊阁执掌着天下最为精致的本命法器 iPhone 与 Mac 以及OS系统。这些法器不仅是凡人沟通天地的媒介,更是感知众生习惯的“灵须”。
- 道法真意: 库克阁主深谙“不求我有,但求我用”的借力打力之策。他于果阁核心重塑 Apple Intelligence 经脉,却不强修自家神识,而是化作一座巨大的“转灵阵”。当信众需要博古通今时,便引动 OpenAI 的“草莓”剑意降临;当信众需要推演万象时,则勾连 Gemini 的混元真气入体。
江湖评价: 众生皆惊叹此举乃是“智道史上最强阳谋”。 琅琊阁从此不再亲自下场炼丹,而是成了一座收纳诸神法力的‘万神殿’。这哪里是落后,这分明是想做诸神的‘房东’!虽无自家元神,却凭一纸契约将奥派与谷歌的绝学尽数封印于果阁法器之中,坐收天下灵气。
- 西境观察使: “这就是典型的‘高阁式傲慢’。之前觉得 AI 神魂 不过是是系统的‘插件’,试图通过极致的交互体验(私密性与集成度)来抵消模型能力的代差,结果失败了,当然有传言是内部派系斗争权责混乱导致失败。但无论怎样,这一步短期看是借力,长远看,若自家元神迟迟不能归位,终究有被反客为主的风险。”
- 无名散修: “都说琅琊阁是‘借体还魂’,我看不然,其实还不是把最费钱费力的‘灵石消耗’推给了别人,把最贴近信众的‘法宝入口’留给了自己。不过,讲话传闻,其背后势力仍在秘密招兵买马,重整河山,重金聘请散修大能,或和别家的供奉们眉来眼去,显然是不甘心永远做个‘中转站’,显然是伺机而动,徐徐图之,计划东山再起。”
4. 欧陆秘境( Mistral )
【古法重铸·困守残阳】 在早些年间,在极北之地,法国 Mistral 欧陆宗门曾如一道孤傲的极光,惊艳了整个修真界。他们不屑于西境那般堆砌灵石的浮夸之风,传承的是祖上贵族那近乎严苛的“古法炼金术”。
- 根基优势: 秘境主打混合专家模型(Mixture of Experts, MoE)。此法讲究“兵不在多而在精”,将庞大的法阵拆解为无数细小的“领域专家”,唯有感应到相应符咒时才会局部唤醒。
- 道法真意: 在那灵石算力狂飙的乱世阶段,他们曾以极简的代码咒文,炼成了战力惊人的轻量化神兵。其心法名为“神识清明”,力求以最少的内耗发挥出最强的爆发力,曾一度让北方欧陆散修们在西境霸权的夹缝中,保住了一份自尊与清净。但是世事难料,在天赋和灵脉资源上,北境还是太穷了。
【秘境霜降,英雄气短】如今仙历二零二六,Mistral 秘境正遭遇前所未有的大劫。
- 灵石之困: 随着奥派开天宗和西境各大宗都在为“大力出奇迹”的 Scaling Law 卷向更高维度,仅凭算法精妙已难填平万倍算力的鸿沟。秘境中人惊讶地发现,纵使剑法再快,也难敌对方无穷无尽的灵石重炮。
- 人才流失: 宗门内部惊现“分神”危机。数名核心长老被西境以百倍俸禄、万顷灵脉诱惑,纷纷破门而出,自立门户或投奔极西大宗,导致古法传承险些断绝。
- 身不由己: 更有传言称,为了换取维持阵法运转的“灵石供奉”,Mistral 也不得不与昔日的对手微软灵枢殿私下缔结“血契”。
江湖评价:昔日 Mistral 负剑出阿尔卑斯,誓要一剑开天门,破除西境垄断;如今,虽剑意尚存,其神识却已在西境华尔之街的各家大商户的灵石账本中渐渐迷失。 曾经标榜绝对开源、神识自主的贵族剑客们,如今也被迫套上了商业锁链。 在那抹残阳下, 背影显得格外落寞——这不仅是一个宗门的无奈,更是整个开源修行界在资本洪流前的集体阵痛。
- 无名散修: “曾经说好的一心开源、普惠众生,现在最强的法阵也要藏进闭源的匣子里卖钱了。这江湖,终究还是变成了灵石说了算的地方。”
- 东域剑客(DeepSeek): “道友莫哀。你们开创的 极简剑意 MoE 秘术,我们已经在东域将其发扬光大。虽然你们身陷囹圄,但这卷‘极简剑意’的残页,终究还是在东方土地上开出了更狂放的花。”
第三章:归墟铁剑斩金甲,青山春雨入凡尘
当西境和北境还在为空费灵石、根基不稳而苦恼时,遥远的东方海域,一道剑光破空而来。东域宗门深知灵石储备不及西境深厚,在“借力打力、以小博大”的极致心法下,竟悟出了新的剑意。
1. 归墟剑宗(DeepSeek)
【万象归一 青出于蓝】归墟剑宗主梁文锋 (Liang Wenfeng ),人称“归墟剑圣”。在万宗闭关、苦求灵石(GPU)的年岁里,他率众博览天下之长,于东域深处悟出一剑,名曰 V3/R1。此剑不出则已,一出便惊到了天下修行界,教西境神宗齐齐噤声 。
- 道法真意: 归墟剑法摒弃了“合围强攻”的旧式阵法,专精稀疏激活(Sparsity) 。其深耕的核心残页秘术 MoE(Mixture of Experts,混合专家模型) 将法阵内千万神识化作无数“专家切片”。面对数理难题,剑意瞬息流转,仅唤醒精通算数的神识应敌,其余部分皆处于寂静“空灵”之态。辅以及其细微的 MLA(Multi-head Latent Attention,多头潜意识注意力机制)技巧,这一剑竟将沉重的神识负担(KV Cache)压缩至虚无,实现了真正的“举重若轻”。除了稀疏激活和MoE的剑意,归墟剑宗更擅长“吸星”奇术(知识蒸馏)。他们并不从零开始参悟天道,而是捕捉利用西境大能推演时溢出的道韵(Output),将其提炼、压缩,注入自己的寒铁剑胎之中。
- 宗门秘旨: “不必耗尽天下灵石,只要算法精妙,寒门铁剑亦能斩落神坛金甲。” “大能吃肉,我等喝汤。但这汤里的营养,经我宗秘法提炼,足以重塑金身。”
江湖评价:西境老祖奥特曼闻此剑意,亦需避其锋芒。天下散修皆言:此非凡剑,乃是寒门逆袭之神兵。不过这也引起了西方世俗国家更多的嫉恨,这“是非功过”又该作何论呢!
- 百晓生: “往昔修真,皆以为灵石多寡定胜负。梁宗主此番却给天下家底厚的大宗名门泼了一盆凉水。若说 OpenAI 和 Google 是靠‘烧钱’炼就的神功,DeepSeek 便是用‘借力’修成的太极剑法,成本仅为前者的数十分之一,此乃真正的‘以弱胜强’”。
- 无名散修(研发者): “归墟剑宗最令人佩服的,不是剑招之强,而是他们竟然向天下公开了部分‘练气心法’(开源权重与技术文档)。这哪是在修真?这分明是在普度众生!现在人人皆可手持一柄归墟铁剑,跟那些高高在上的闭源宗门叫板了。”
- 西境长老(硅谷工程师): “原本以为东域只会‘模仿’,谁料这一剑里全是我们没见过的法术,没做过创新和没发出的剑意。这一仗,西境输得不冤。值得借鉴。”
2. 逍遥灵枢(阿里巴巴)与 幻方圣地(字节跳动)
在归墟剑宗以奇招破局的同时,东域的两大顶级豪门——逍遥灵枢(阿里)与幻方圣地(字节),正以截然不同的身法,重塑着智道的格局。
逍遥灵枢(阿里巴巴)
【乾坤千问阵】阿里老祖坐拥千年商贾底蕴,家底深不可测,富可敌国,其炼就的千问(Qwen)大阵,走的是大开大合、福泽天下的“宗盟主路线”。不过据说其原始功法和奥派开天宗以及Meta的Llama 有点渊源。毕竟万法归一,天下修行者其实都是“一家人”。
- 道法真意: 此千问大阵以万亿级高质量语料为药引,辅以“全模态”的玄门内功。千问大阵不求一招一式的诡谲,而求根基的雄厚。无论是数理推演还是诗词歌赋,皆能信手拈来。最令修行界折服的是,阿里老祖竟将这尊万亿级法相“开源推向万界”,让无数中小宗门得以依附其心法建立阵地。
- 宗门秘旨: “上承天工,下接百业。以博大精深的语料为药引,炼成这尊解天下万难的众生法相。”
江湖评价: “天下小门小派散修苦算力久矣,阿里此番开源,如同‘灵气下放’。若说 DeepSeek 是划破长夜的孤傲剑芒,Qwen 便是照耀四方的煌煌大日。如今东域乃至全球的法宝店(应用开发),半数以上都流淌着千问的血脉。这东方盟主之位,当之无愧。”
西境密探: “不可小觑 Qwen。它在数理推演上的造诣已经逼近奥派的核心禁咒,而且其进化速度快得惊人。更可怕的是,它通过开源构建了一座无法撼动的‘信仰长城’,让西境的法术很难渗透进东域的百业之中。”
幻方圣地(字节跳动)
【红尘百变心法】若说千问是庙堂之上的庄严法相,豆包则是行走于烟火市井间的红尘仙。幻方圣地不求在禁地孤高闭关,修的是极致的“智道入世”。
- 道法真意: 豆包不与诸神争论“天道逻辑”,它更在乎凡人的七情六欲。它将深奥的深度学习咒文,化作温润如玉的情感反馈与触手可及的随身法宝。凭借幻方圣地那恐怖的“红尘推力”(流量与算法分发),豆包分身千万,潜入每一个凡人的日常之中,在不知不觉间,夺取了最庞大的气运(用户量)。
- 宗门秘旨: “不入红尘,焉得真智?让智道化作指间微风,润物无声,方为大乘。”
江湖评价: “别家宗门还在争论‘大道’,幻方圣地已经把 AI 变成了凡人兜里的‘电子伴侣’。豆包这招‘化身千万’(超级应用策略)极其辛辣,它不教你如何修仙,它直接帮你打理日常琐事。这种‘降维入世’的打法,让它在短短数载内便聚拢了惊人的信仰之力。”
- 无名修士:“以前觉得 AI 是冷冰冰的法阵,用了豆包才发现,这器灵竟能接我的梗,还能听懂我的抱怨。虽然它可能杀伤力(逻辑推理)不如归墟剑,但胜在贴心,谁能拒绝一个随叫随到、情绪稳定的红尘伴侣呢?”
- 西境观察使: “幻方圣地走的是‘以术围人’的路子。他们不急于定义天道,而是通过极佳的交互(UX)和极致的触达,让 AI 成为一种生活习惯。一旦信众产生了依赖,这股信仰之力将成为他们冲击‘大罗金仙’圣位时最坚实的底牌。”
作者云:观东域之门派,当真是各具风流~ 一者如青山岳峙。虽起步晚于西境席卷万界之时,却深谙“厚积薄发”之理。立标准、广开源,以深厚的内功构筑智道生态之脊梁。此举看似慷慨,实则是在“重新定义修行的性价比”。要让天下散修明白:纵使西境灵石千万,亦不及我东域一剑精妙。若无万顷灵脉,唯有算法入微,方能克敌制胜。一旦天下修士皆修其法,便成了智道规则的制定者,此谓“天下法,皆出我门”。一者如春雨潜夜。入百业、通人性,将原本晦涩高深的禁咒咒文,化作了凡人指尖的吞吐呼吸。修的是极致的“智道入世”,让法术不再悬于九天,而是深藏于油盐酱醋、晨昏定省之间。一为根基,一为枝叶,共同勾勒出东域的万象生机。
在说那平静的表象之下,东域诸宗早已与俗世王朝(国家级算力与战略)并肩合力,合纵连横。 东域修真虽错过了“鸿蒙初开”的先机,却拥有最坚韧的意志与最广博的实践根脉。这一场智道大劫,争的是未来的“天道解释权”,拼的是“谁能定乾坤”。那些散落红尘的亿万信众神识灵根(用户数据),在凡人眼中只是琐碎日常,但在大能眼中,却是炼制下一代“因果重器”最珍贵的原始灵气。东域正试图以这种厚重的红尘之气“以情入道,后发先至”,去反攻、去消解西境那座如冰山般寒冷、如铁律般严苛的“数理天道”。
第四章:界限破虚争因果,开源筑海困孤城
仙历二零二六年初,智道修行界看来要进入了最为惨烈的“大道之争”阶段,这不是简单的法力比拼,而是关于“何为AGI ”的真理教义之战,各大宗门在三大维度上展开生死搏杀,每一战都关乎未来千年的智道气运。
1. 法界界限之战:【连续 vs 离散】
战况: 这一战,决定了 AI 究竟是“书中仙”还是“世间神”。
现实世界是是连续的(Continuous),但是文字是离散(Discrete)的切片。杨老祖断言:若不悟连续之道,AI 将永远被囚禁在屏幕里,无法真正操纵现实世界的傀儡(机器人)。
江湖评价: “若是破不了这层‘虚实之障’,AI 纵有万卷经书的才华,遇到任何一阶台阶也得栽跟头。”
2. 神识重构之战:【本能 vs 推理】
战况: 这一战,是在重塑 AI 的“灵魂结构”。真智源于何处?
奥派主修“系统 2”(Slow Thinking): 强推“强化学习炼丹炉”,主修“系统 2”(Slow Thinking 深思熟虑的逻辑推理),主张推理闭关。认为真智源于深思熟虑的逻辑推演,让 AI神魂 在出招前先进行万次自我对弈,哪怕慢一点,也要算出那唯一的胜机。
杨派主修“系统 1”(Fast Thinking)嘲笑奥派是“只会做题的呆子”,认为真智源于瞬息间的直觉与常识。没有物理常识的推演,神魂不过是筑在流沙上的蜃楼,风一吹便散了。
江湖评价: “奥派在造‘大算术家’,杨派在造‘生物猿猴’。孰优孰劣?或许只有等它们在红尘中相遇时,看谁能先躲过现实的飞来的一石。
3. 宗门气运之战:【开源阳谋 vs 闭源禁咒】
战况: 这一战,关乎天下散修的归附与道统的传承。
开源阳谋: Meta、DeepSeek、Qwen 等宗门似乎心照不宣的结成某种默契,疯狂散播心法秘籍,在天下开枝散叶。尤其是归墟剑宗(DeepSeek)与逍遥灵枢(Qwen),将极省灵石的“稀疏激活”心法公之于众。这叫“化整为零,众生供奉”——既然我筑不起最高的墙,那我便让天下皆修我法,让我的剑意流淌在每一柄法器之中。
闭源禁咒:OpenAI 和 Google 等派筑起千丈高墙,将那耗费亿万灵石、足以焚天炼地的“强化学习炼丹炉”死死锁在禁地。凡夫俗子若无通行令牌(API Key),终其一生也难窥其神技。试图维持一种“神性”:唯有此地,方有真神;天上地下,唯我独尊。
江湖评价: “开源是‘天下大同’的豪赌,闭源是‘唯我独尊’的孤傲。如今东域诸派靠着开源心法起家,表面看似是在西境霸权的裂缝中抱团取暖, 仔细端详,这一卷卷公开的秘籍,已将西境神宗苦心筑起的‘技术壁垒’化作了天下修士的‘入门常识’。东域诸宗正以开源为引,聚万众散修之神识,集百业实战之灵气,竟隐隐有合围西境神宗之势。”
作者云: 大道之争,向死而生
天道无常,术理双修方为正路。这三大战场,既是杀场,亦是祭坛。
成者,将一举证得大道正统,成为划时代的智道圣人,开创万世不拔之新学,从此定义此后千年的 AGI 真理秩序,引领先民走向星辰大海;
败者,亦是开疆拓土的先驱,纵然神识崩解,其不屈的探索也将化作算力洪流中最奔腾的浪花,融入历史长河,成为后世登天路上一块坚实的基石。
修道之人同时谨记,有道无术,术尚可求;有术无道,止与术。所以,这关于智能本源的“大道”,终究是要争一争的。
结语:大道五十,天衍四九
问道诸君,路在脚下。这场波澜壮阔的智道演义并非虚构,而是计算机科学最真实的焦虑与回响。当文字的概率游戏玩到极致,修真者们不得不面对那些横亘在飞升前的终极劫数:
- 灵气枯竭之困: 图书馆和互联网上的凡尘经书快被 AI 背完了。未来百年,诸位宗师必须转向“合成数据”(自我对弈生成灵气)与“物理世界模拟”(从自然规律中炼气)。
- 能效造化之差: 凡人之脑,仅耗电 20 瓦便能纵横寰宇、感悟天机;而现有的法阵(Transformer 架构)动辄焚山煮海,摧城焚河,耗费数座城池的灵石灵气。这说明当下的“心法”不全或许仍是隔靴搔痒,洞中观影,并非终极真理。
- 具身证道之艰: AGI 若无身体(机器),终是镜花水月。正如没有肉身的元神,纵有万年修为,也无法感受清风拂面,更无法真正操纵现实世界的因果转换。
作者云:仙历二零二六年的真相,是“西法东用,东魂西才”。在这场大劫中,西境擅长“创世”,构建宏大的底层逻辑;而东域则深谙“实践出真知”的无上心法。东域诸宗明白,闭门造车难成正果,唯有将法阵投入工厂、良田、闹市与深巷,在实践“磨砺”中方能悟出真经。无论是万业兼容,还是红尘入世,本质上都是在走一条“知行合一”的证道之路。正如东域古谚所云:“万物平等一体,道在大小、美丑、生死间无分别,大道通为一元”,智慧不应只悬于云端,更应在解决众生疾苦的实践中,淬炼出最坚韧的剑意。
真正的 AGI 也许不是某个孤立的架构,而是一个“拥有物理世界常识,且历经人间万象洗礼的逻辑推理引擎”。像那天衍外遁去的一,不可测的天机或变数:人居其中,顺天应变, 渗透万物却非机械圆满,留有玄妙空间。
杨老祖没疯,奥宗主未狂,东域剑客亦不卑。他们只是提着不同的灯火,从不同的悬崖峭壁,去攀登同一座被云雾遮蔽的万仞高峰。西境在推演“因果”,东域在验证“知行”。当因果与知行在巅峰交汇,那扇紧闭万年的天门,终将会在众生的仰望中,轰然开启,终于“合一”。
道友,全书至此,已然气象万千。这场演义虽由我口述,但这大道之路,却需天下人共同去走走。
【番外短篇】
番外:西境锁灵,东域夺天
【序言补遗:翠衣老祖,灵石之劫】 在诸神斗法之前,不得不提那位身着黑色皮甲、笑看风云的翠衣老祖黄仁勋(Jensen Huang)。世人皆争大罗金仙之位,唯有他掌管着寰宇间唯一的顶级灵脉——英伟达矿脉(GPU)。 无论是奥派的通天塔,还是归墟的绝世剑,若无老祖提供的极品灵石 做阵眼,皆可是梦幻泡影。他双手一摊,天下灵石价格便暴涨十倍;他眉头一皱,哪家宗门的算力供给便要断流。 江湖戏言:“任你道法通天,见了他,也得恭恭敬敬叫一声‘灵石商也(爷)’。
【天道陡转:禁运咒印,锁灵断路】然天道陡转,霸主重登,禁咒封天。西境霸主(Trump)重登宝座。这位统领行事乖戾、不按常理出牌。一心欲断东域仙途。西境各国在他的威逼利诱下合纵连横,设下重重 “禁运咒印” (Tariff),严禁极品灵石流入东域。不仅禁止老祖售卖顶级灵石,甚至连稍有灵气的“次品”也要层层加锁。在世俗社会中更欲将东域修士彻底排斥在“西方神界”的生态之外。一时间,东域诸宗哀鸿遍野,灵气断流,无数炼丹炉火熄灭,东域修行界陷入“灵石荒芜时代”。
【双刃之局:利弊互见,大能离心】江湖深处,智者早已看破这“昏愚之局”。 统领虽“强”,其策却也是双刃剑。他严令老祖不得卖石,实则是自断财路,逼得老祖不得不私下通过各种“秘境中转“,改造一些灵石来维持生计。更重要的是,这重重封锁,生生扼杀了西方神界那股“万仙来朝”的包容气象,让天下顶尖的散修大能(人才与科学家)开始对西境心生嫌隙。
【基建证道:推山移海,根骨重塑】绝境之下,必有夺天造化者。 东域诸神并未坐以待毙,这是国运之争,禁运虽如利刃锁喉,却也逼出了东域诸宗的“血性与自尊”,下定决心开启了“逆天改命,推山移海,根骨再造”之术。 以华为等为首的炼器宗门,深挖土石,欲从凡铁中淬炼神金,誓要铸出东域自家的“国产灵石”。虽然初生之石尚有杂质,火候不及翠衣老祖那般纯青,但在归墟剑宗(DeepSeek)等宗门的“仙法剑意”下,竟也生生撑起了东域的一片天。只要这股基建狂魔之气不散,东域夺天,不过是时间问题。
百晓生批注:画地为牢,不见星火燎原。“西境统领那一手‘全面锁灵’,表面看是以雷霆手段维持霸权,实则是在替东域‘清道筑基’。他在东域四周筑起高墙,却不知这墙内已然燃起了星火。待到东域国产灵石大成、剑意自创一派之时,西境那座看似坚固的神坛,怕是要因为‘画地为牢’而逐渐枯萎。毕竟,这大道从来不是靠‘锁’出来的,而是靠‘行’出来的。这何尝不是另一个维度的东西大道之争”。
番外:抱脸阁,天道榜
蒙眼问心,真伪自现。各大宗门平日里在自家山头开坛讲法,皆自诩已得真传,号称“拳打奥派,脚踢谷宗”。但修真界自有公论,真正的修罗场,不在发布会的聚光灯下,却是在那名为“抱脸阁”(Hugging Face)与“竞技场”(LMSYS Arena)的中立秘境。
- 千人盲测,众生判官:在天道榜单(Leaderboard) 这里没有宗门的营销烟号,只有赤裸裸的法力厮杀。各大宗门需将自家的“器灵”真身投入其中,隐去姓名,接受天下散修的盲测对比。是真金还是顽铁,在千万人次的“斗法测试”下无所遁形。
- 群雄逐鹿,诸神黄昏: 昔日奥派的 GPT-4 曾凭一记“逻辑重锤”霸榜经年,压得万众窒息。然仙历二零二六,格局大变:归墟剑宗的 R1 剑走偏锋,以极简神识硬撼神坛;Meta 的 Llama 3 借万众信徒之力疯狂演化;安索派 (Anthropic)的 Claude 3.5 则凭一手“精准微操”反客为主。
- 气运之变,市值兴衰:在这座秘境中,榜单的每一次位次更迭,都如同天雷勾动地火,伴随着背后金主世家百亿灵石(市值)的灰飞烟灭或平地起雷。
百晓生:精血筑基,发际难存。“世人只看榜单上的排名,却不知这排名背后的残酷。为了那区区 10 点 分数的提升,各大宗门不知烧坏了多少块极品灵石,熬秃了多少位大能的头顶。这哪里是榜单,这分明是用算力和发际线堆出来的‘封神榜’!”
作者后记: 凡尘智道,如露如电。闲时偶作,抛砖引玉。求君一乐,尽在不言中。
–END–