Reinforcement learning (RL) is a machine learning technique where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The agent performs actions and receives feedback as rewards or penalties. It aims to maximize cumulative rewards over time.
Gen AI Podcasts (Reinforcement Learning Study):
Tools: Google Notebook LM
Content: Reinforcement Learning 2nd R.Sutton and A. Barto; The Reinforcement Learning Framework (Hugging Face); Stanford CS234: Reinforcement Learning | Winter 2019.
Key components of RL include:
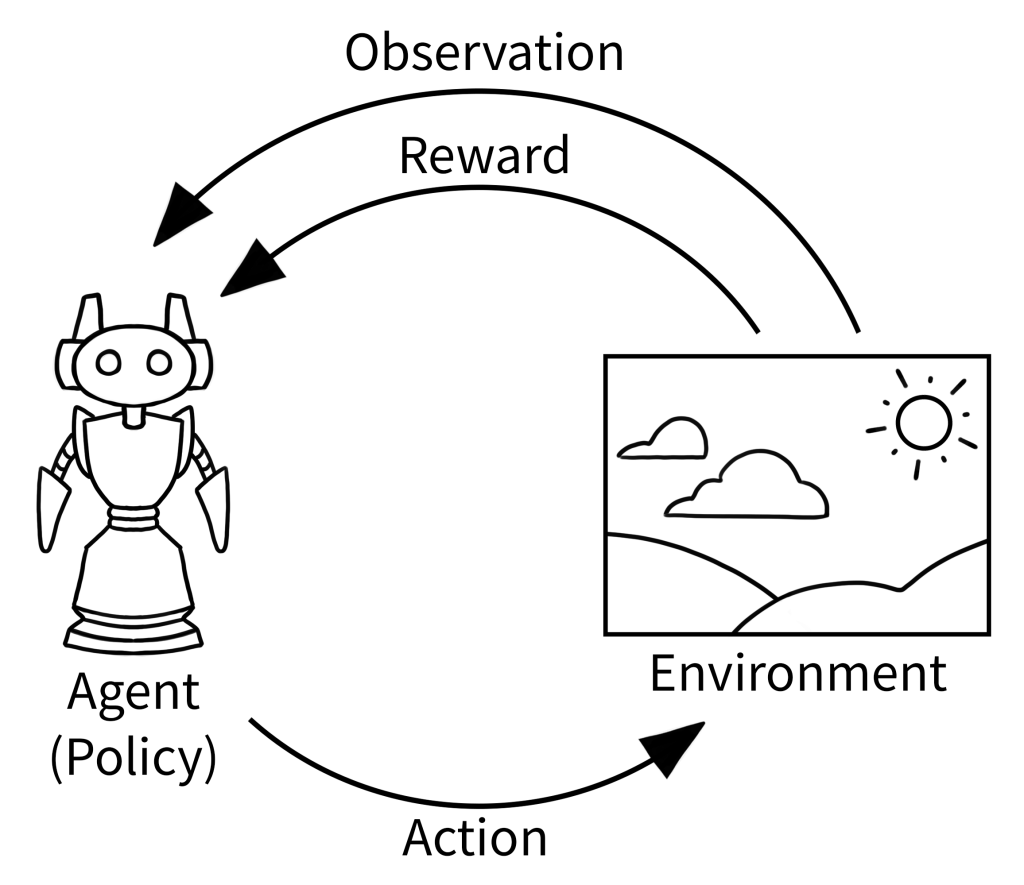
- Agent: The learner making decisions
- Environment: The world the agent interacts with
- State: Current situation of the environment
- Action: Choices available to the agent
- Reward: Feedback signal indicating action quality
Unlike supervised learning, RL doesn’t rely on pre-labeled datasets but learns through trial and error.
RL is used in various applications. These include robotics, game playing, and autonomous systems. It enables adaptive decision-making in complex, dynamic environments. The classic algorithms in reinforcement learning are primarily categorized into three types: Value-Based, Policy-Based, and Model-Based methods.
Here are some representative classic algorithms:
Value-Based Algorithms
- Q-Learning: A model-free, off-policy algorithm that uses the Bellman equation to estimate the optimal action-value function.
- SARSA (State-Action-Reward-State-Action): It is a model-free, on-policy algorithm. This algorithm uses the Bellman equation to estimate the action-value function. However, it is based on the expected value of the next action.
- Deep Q Network (DQN): A deep learning version of Q-Learning that uses neural networks to approximate the Q function.
Policy-Based Algorithms
- Policy Gradient: Directly selects actions based on the current state, choosing behaviors through observational information and performing backpropagation.
- TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization): An improved policy gradient method.
Algorithms Combining Value and Policy
- Actor-Critic: Combines value-based and policy-based methods. The Actor makes actions based on probabilities. The Critic provides values based on those actions.
- A2C (Advantage Actor-Critic): A variant of Actor-Critic.
- A3C (Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic): An asynchronous version of A2C.
Other Important Algorithms
- DDPG (Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient): An algorithm suitable for continuous action spaces.
- PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization): An improved policy optimization algorithm.
These algorithms have wide applications in game AI, robot control, autonomous driving, and other fields. Each algorithm has its characteristics and applicable scenarios. For example, Q-Learning is suitable for handling large continuous state spaces, while SARSA excels in dealing with stochastic dynamics problems.

